Mixed-Reality Platform for Simulation and Synthesis of Multi-Modal Hallucinations with Applications to Schizophrenia Treatment

Treating patients with schizophrenia for auditory hallucinations has traditionally required multiple trials of antipsychotic medications, to which approximately one in three patients are resistant. An alternative, Avatar Therapy, has been shown to effectively reduce the distress and helplessness associated with auditory hallucinations. While Avatar Therapy holds great promise, there are many open questions as to the requirements for optimal delivery of this treatment. Similarly, many potential enhancements to how avatars are rendered to the patient remain to be tested. Exploration of these questions and enhancements requires development of a mixed reality platform that offers to the therapist the ability to easily adjust various parameters of the avatar(s). We will iteratively design, implement, and test such a platform, and then apply the knowledge gained to an augmented reality version of the platform suitable for use outside of the therapist’s office. The resulting intelligent medical device will offer the possibility of providing therapeutic benefits to patients in their day-to-day activities.
Avatar Creation
Our present avatar creation pipeline consists of three phases:
- Graphical exploration through a GAN-based image map.
- Voice transformation to approximate the sound of the patient’s hallucination.
- Mapping of the graphical avatar to a 3D model for animation control.
Haptic Simulation
Since increased sensory immersion is associated with higher effectiveness of avatar therapy, we are quantifying the added benefit of supplemental haptic representations.
For this purpose, we are developing pneumatically actuated finger-style devices that deliver force sensations evocative of human touch.
Biosignals Processing
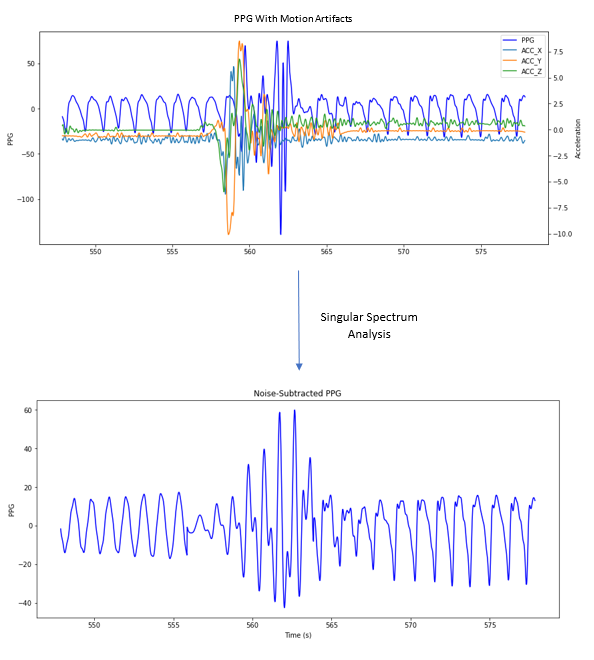
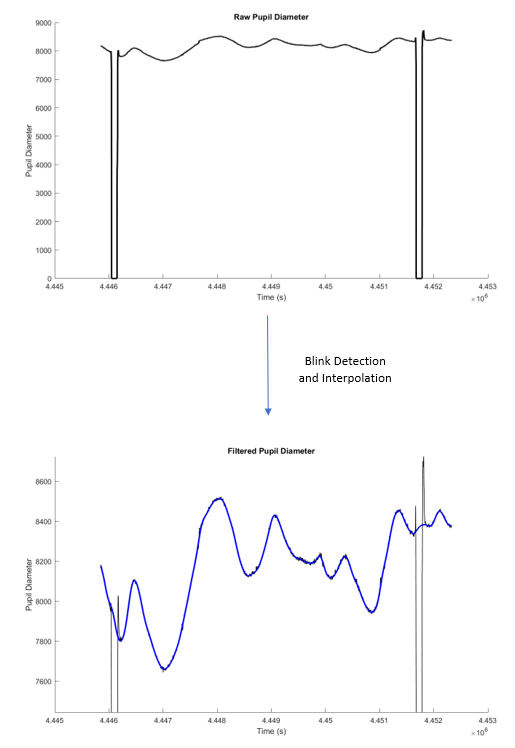
Beyond self-report, objective evaluation of therapeutic effectiveness is planned through biosignal analysis.
- PPG data: filtering motion artifacts to extract heart rate variability (HRV), a biomarker associated with stress and hallucination episodes.
- Eye-tracking: filtering blink activity from pupil diameter measurements to explore ocular biomarkers of engagement and cognitive load.
References
- Barnes, T.R.E., Buckley, P., & Schulz, S.C. Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia. John Wiley & Sons, 2007.
- Craig, T.K.J., et al. “AVATAR therapy for auditory verbal hallucinations in people with psychosis: a single-blind, randomised controlled trial.” The Lancet Psychiatry 5.1 (2018): 31-40.
- Leff, J., et al. “Avatar therapy for persecutory auditory hallucinations: What is it and how does it work?” Psychosis, 6:166-176, 2014.
- Dellazizzo, L., et al. “Avatar therapy for persistent auditory verbal hallucinations in an ultra-resistant schizophrenia patient: A case report.” Frontiers in Psychiatry, 2018.
- Percie du Sert, O., et al. “Virtual reality therapy for refractory auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia: A pilot clinical trial.” Schizophrenia Research, 2018.
- Llorca, P.M., et al. “Hallucinations in schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease: analysis of sensory modalities and patient impact.” Scientific Reports 6, 38152 (2016).
- Zimmermann, G., et al. “The effect of cognitive behavioral treatment on the positive symptoms of schizophrenia spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis.” Schizophrenia Research 77(1):1-9, 2005.